Contents
Testosterone Therapy
 Tens of thousands of men in their late 30s and 40s are trying testosterone shots, gels, and patches these days in hopes of regaining virility and youthful vigor. The fact that more than 1.75 million prescriptions for testosterone products were written in the year 2002 suggested there was a 170 percent increase from 1999. The numbers have been growing at an astonishing pace and it is estimated that more than 4.6 million prescriptions were written in the year 2010 for testosterone products.
Tens of thousands of men in their late 30s and 40s are trying testosterone shots, gels, and patches these days in hopes of regaining virility and youthful vigor. The fact that more than 1.75 million prescriptions for testosterone products were written in the year 2002 suggested there was a 170 percent increase from 1999. The numbers have been growing at an astonishing pace and it is estimated that more than 4.6 million prescriptions were written in the year 2010 for testosterone products.
Why Testosterone Replacement Therapy?
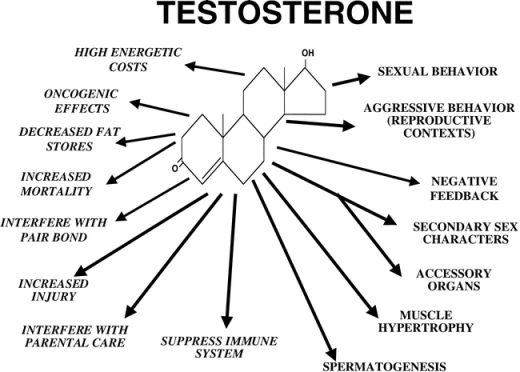
Testosterone is a naturally-producing steroid hormone that is responsible for the proper development of male sexual characteristics. It is also responsible to maintain muscle bulk, adequate levels of red blood cells, bone density, sense of well-being, and sexual and reproductive function.
When the human body is not able to produce enough of natural testosterone, functions of the body get disrupted. Testosterone replacement therapy is recommended when erectile dysfunction (ED) occurs with decreased testosterone production.
Factors Causing Testosterone Deficiency
The amount of testosterone in the human body gradually declines with growing age. This “natural decline” starts after the age of 30 years and continues throughout life.
Some of the other causes of testosterone deficiency are:
- Chemotherapy or radiation treatment for cancer
- Injury or infection to the testicles
- HIV and AIDS
- Cirrhosis of the liver
- Chronic renal (kidney) failure
- Hormone analogues used for treating prostate cancer and steroids
- Genetic abnormalities like Klinefelter’s Syndrome (extra x chromosome)
- Chronic illness
- Congenital conditions
- Stress and inflammatory diseases
Symptoms Of Testosterone Deficiency
The symptoms of testosterone deficiency include the following:
- Depressed mood
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased sex drive
- Difficulties with memory and concentration
- Decreased sense of well-being
Some of the possible changes that occur in the human body with deficiency of testosterone are fragile bones (osteoporosis), decrease in body hair, variable effects on cholesterol metabolism, increase in body fat, decrease in muscle mass, decrease in hemoglobin, and possibly mild anemia.
How Do I Find Out If I Have A Testosterone Deficiency?
The only accurate way of detecting testosterone deficiency is to have your medical practitioner measure the amount of testosterone in your blood. It is important to note that doing this may involve several measurements since the levels of testosterone tend to fluctuate throughout the day, with the highest levels usually recorded in the morning.
Testosterone Test At The Hospital
It is highly recommended that you help your doctor by offering a detailed and accurate medical history. In order to get the medical history, the doctor would be seeking details about your past or present illnesses, any sexual problems you are having, recent events that may have caused stress, all prescription and non-prescription drugs you are taking, and if any one in the immediate family is suffering from a genetic disease.
Thereafter, the doctor may request you to undergo a bone density test and physical examination. If required, testosterone replacement therapy may be recommended by the doctor to make up for low testosterone levels.
Testosterone Replacement Options
An individual found to be short of testosterone could avail the following options:
- Testosterone patches, which are worn either on the body or on the scrotum. These patches are used on a daily basis and the patch application is rotated between the buttocks, back, arms, or abdomen.
- Intramuscular injections, usually every two or three weeks.
- Daily application of testosterone gels that are applied to the upper arms, shoulders, or abdomen.
- Gum tablets, or buccal medications, are the newest form of testosterone therapy in which a tablet is placed between the gums and the upper lip, every 12 hours that gets absorbed into the blood and released slowly. Gum tablets users can kiss women and children while using the tablets.
Note: Testosterone replacement therapy is NOT recommended to individuals who have already been diagnosed with prostate or breast cancer. It is also recommended that all men considering the therapy should undergo screening before starting this therapy.
Changes After Testosterone Replacement Therapy
The effects of testosterone therapy include the following:
- Increase in red blood cells (RBC)
- Increase in sex drive
- Increased body musculature
- Increased body hair growth (notably on chest, arms, legs, belly, and back)
- Facial hair growth (beard or moustache growth)
- Thickening of the vocal chords and deepening of the voice
- Increased activity of the skin’s oil glands (acne or oily skin)
- Increase in energy level
- Increase in appetite
- Increase in muscle mass and bone density
- Reduced anger, fatigue, and depression
It is important to note that changes after testosterone replacement therapy are cumulative in nature, which means that they build gradually over time.
Side Effects Of Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Testosterone replacement therapy is generally safe but has sometimes been associated with side effects, including:
- Decreased testicular size
- Worsening of sleep apnea
- Decreased urine stream or frequency
- Acne or oily skin
- Mild fluid retention
- Stimulation of prostate tissue
- Breast enlargement
- Changes in cholesterol concentrations
Last but not the least, it is important for you to note that testosterone replacement therapy is not for every man. It is NORMAL to lose interest in sex and experience fewer spontaneous erections with growing age and only a qualified doctor could determine if testosterone therapy is right for you.
Symptoms of Testosterone Deficiency




